5.2.1. Description
This study is focused on the verification of component based finite element method (CBFEM) for the resistance of the symmetrical double splice bolted connection to analytical model (AM).
5.2.2. Analytical model
The bolt resistance in shear and the plate resistance in bearing are designed according to Tab. 3.4 chapter 3.6.1 in EN 1993-1-8:2005. For long connection is considered reduction factor according to cl. 3.8. Design resistance of connected members with reductions for fastener holes is considered according to cl 3.10.
5.2.3. Verification of resistance
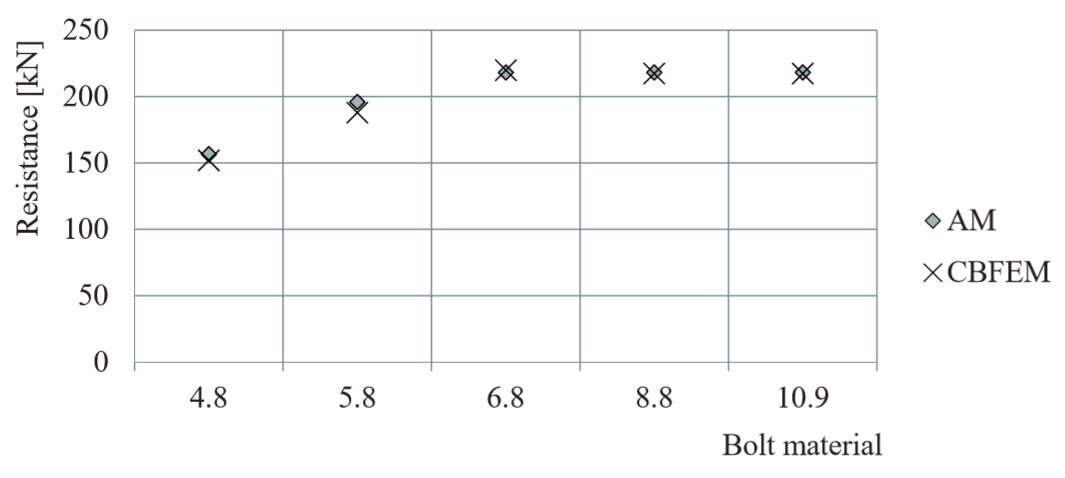
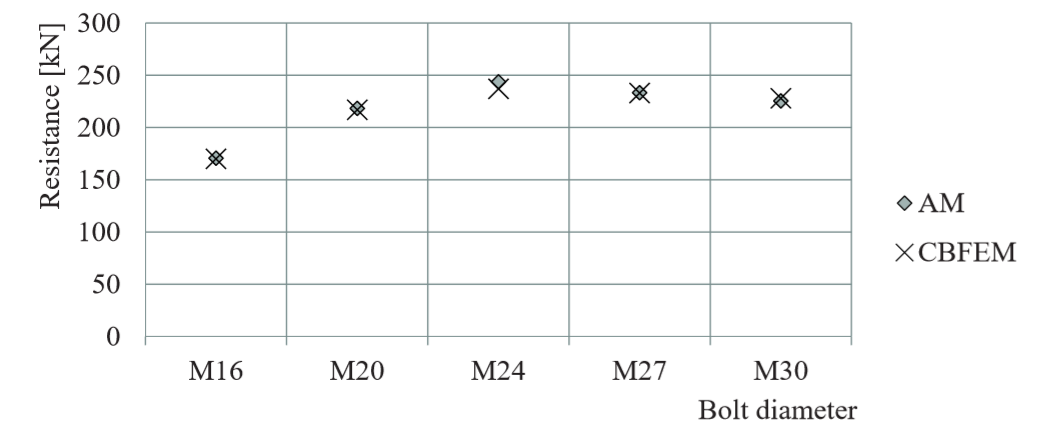
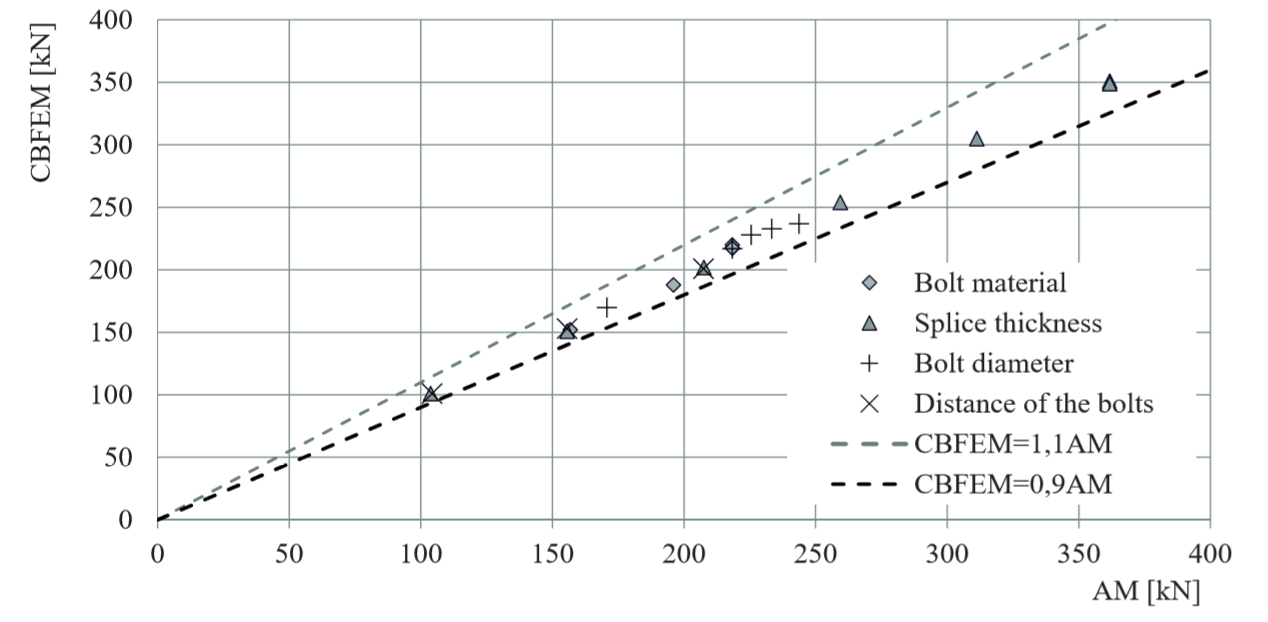
Design resistances calculated by CBFEM were compared with results of analytical model (AM). Results are summarised in Tab. 5.2.1. The parameters are bolt material, splice thickness, bolt diameter and bolt distances, see Figs. 5.2.1 to 5.2.4.
Fig. 5.2.1 Sensitivity study for the bolt material
Fig. 5.2.2 Sensitivity study for the splice thickness
Tab. 5.2.1 Sensitivity study of resistance
Fig. 5.2.3 Sensitivity study for the bolt diameter
Fig. 5.2.4 Sensitivity study for the distance of bolts
The results of sensitivity studies are summarized in graph in Fig. 5.2.5. The results show that the differences of the two calculation methods are up to 5 %. Analytical model gives generally higher resistance.
Fig. 5.2.5 Verification of CBFEM to AM for the symmetrical double splice connection
5.2.4. Benchmark example
Inputs
Connected member
- Steel S235
- Splice 200/10 mm Connectors
Bolts
- 3 x M16 8.8
- Distances e1=40mm, p=55mm 2 x splice
- Steel S235
- Plate 380x200x10
Outputs
- Design resistance FRd = 254 kN
- Critical is bearing of the connected splice
Fig. 5.2.6 Benchmark example of the bolted splices in shear