4.4.1 Description
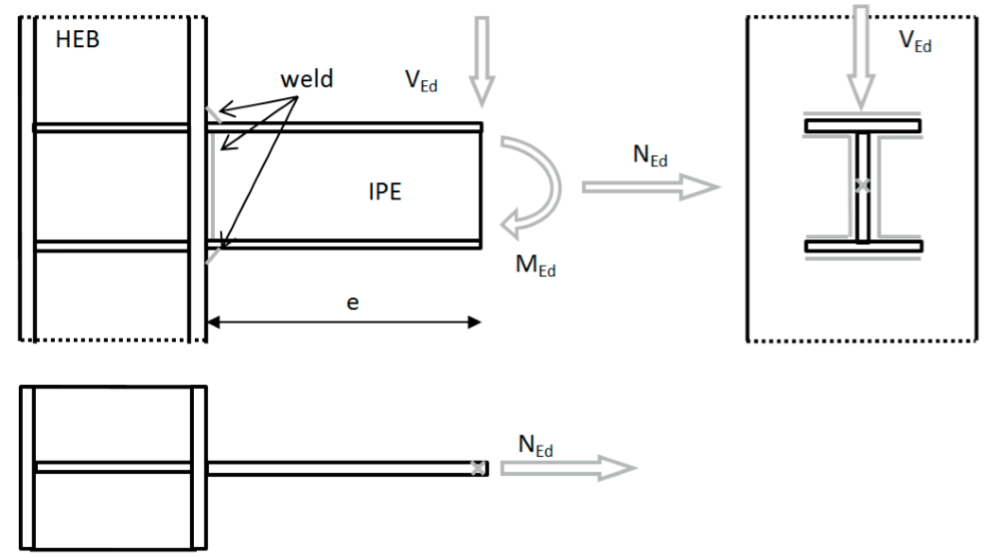
The object of this chapter is verification of component based finite element method (CBFEM) for a fillet weld in a stiffened beam-to-column joint with component method (CM). An open section beam IPE is connected to open section column HEB400. The stiffeners are inside column opposite to beam flanges. The beam section is the changing parameter. Three load cases are considered, i.e. the beam is loaded in tension, shear and bending.
4.4.2 Analytical model
The fillet weld is the only component examined in the study. The welds are designed according to Chapter 4 in EN 1993-1-8:2005 to be the weakest component in the joint. The design resistance of the fillet weld is described in section 4.1. Overview of the considered examples and the material are given in the Tab. 4.4.1. A geometry of the joint with dimensions is shown in Fig. 4.4.1.
Tab. 4.4.1 Examples overview
4.4.3 Numerical model
The weld in CBFEM model is described in section 3.4.
Nonlinear elastic-plastic material is used for welds in this study. The limit plastic strain is reached in longer part of the weld and stress peaks are redistributed.
Fig. 4.4.1 Joint’s geometry with dimensions
4.4.4 Verification of resistance
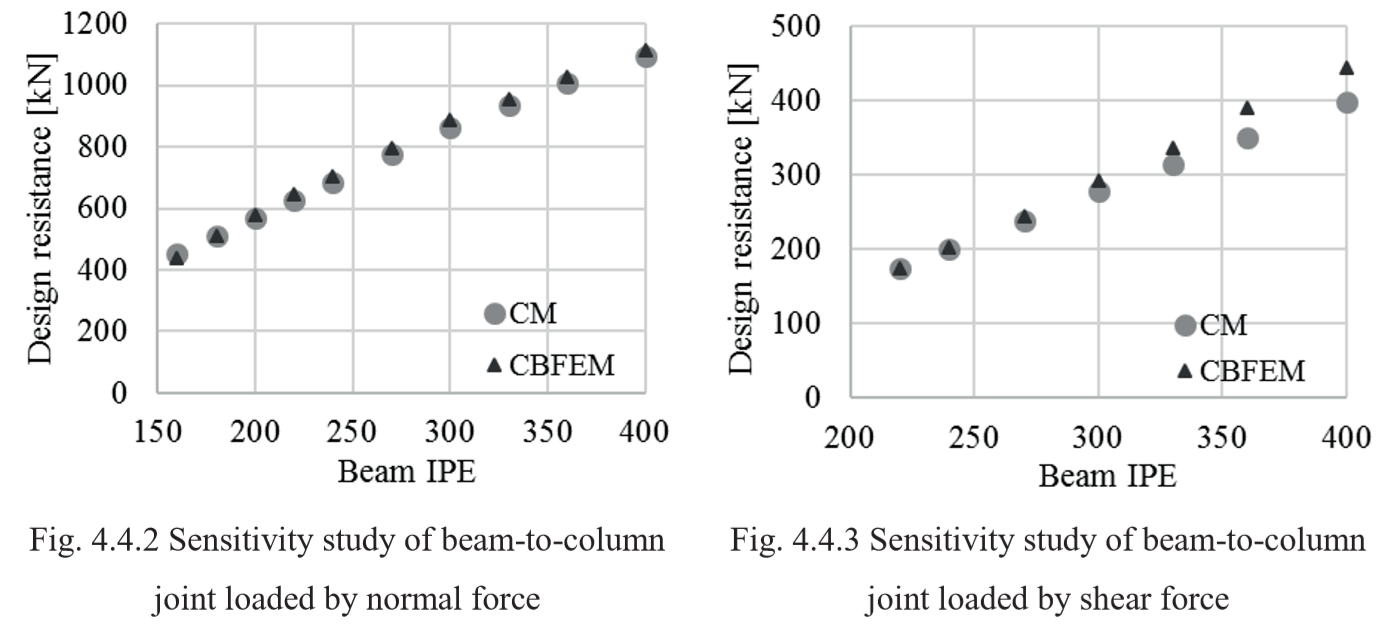
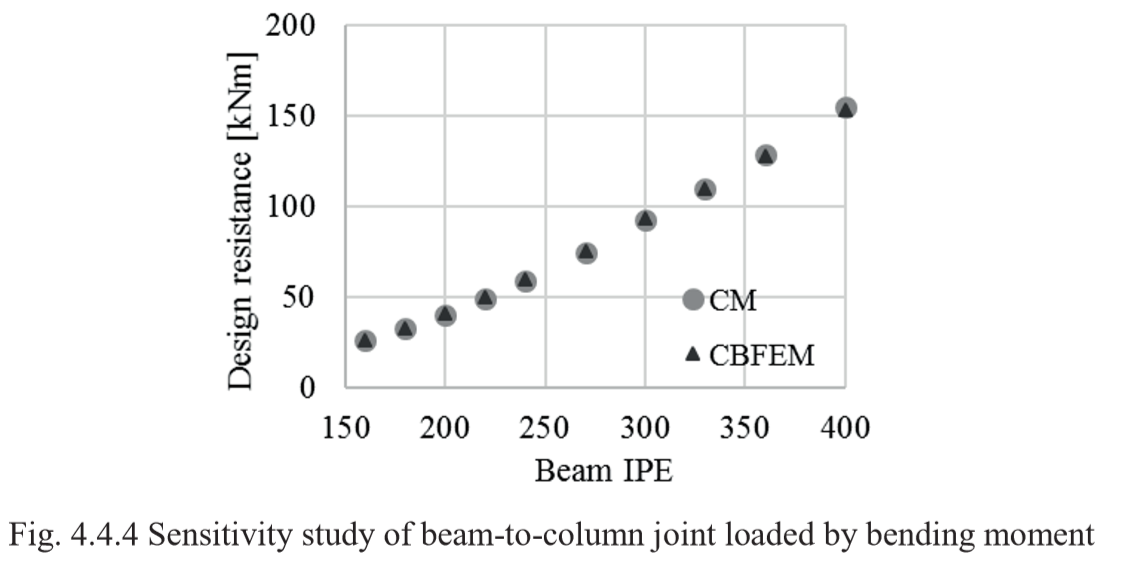
Design resistance calculated by CBFEM Idea RS software is compared with the results of CM. The weld’s design resistances are compared, see Tab. 4.4.2. The study is performed for one parameter beam section and three load cases: normal force NEd, shear force VEd and bending moment MEd.
Tab. 4.4.2 Comparison of CBFEM and CM
Results of CBFEM and CM are compared and a sensitivity study is presented. The influence of beam cross-section on the design resistance a welded beam-to-column joint loaded in tension is shown in Fig. 4.4.2, in shear in Fig. 4.4.3 and in bending in Fig. 4.4.4. The study shows good agreement for all applied load cases.
To illustrate the accuracy of the CBFEM model, results of the sensitivity study is summarized in a diagram comparing CBFEM’s and CM’s design resistances, see Fig. 4.4.5. The results show that the difference of the two calculation methods is in all cases less than 10%.
4.4.5 Benchmark example
Inputs
Column
- Steel S235
- HEB400
Beam
- Steel S235
- IPE270
- Length L = 200 mm
- Force eccentricity to weld x = 400 mm, see Fig. 4.4.6
Column stiffeners
- Thickness ts = 10 mm
- Width bs = 140 mm
- Related to beam flange, position upper and lower
Weld
- Throat thickness aw = 3 mm
Outputs:
- Design resistance in shear VRd = 244 kN
Fig. 4.4.6 Benchmark example of the welded beam to column joint with force eccentricity